India’s Soybean Imports: Brazil Monopolizes
Talk to our team about AgFlow's offering →
Reading time: 2 minutes
India, a nation with a rich agricultural heritage, has always been a significant player in the global agricultural market. Yet, in the first seven months of 2023, the dynamics of India’s soybean imports have witnessed some intriguing shifts. What are the key factors influencing these changes? And what challenges do they present to both the general public and professionals in the agricultural commodity industry?
Key Factors Impacting Soybean Imports
1. Global Supply Chain Disruptions: The aftermath of the global pandemic has left an indelible mark on international trade. With shipping delays and logistical challenges, soybean import costs have surged. This, in turn, affects the price of soybean-based products in India. Is the nation ready to bear these increased costs, or will we see a shift toward alternative commodities?
2. Domestic Production: India’s own soybean production has faced its set of challenges. Unpredictable weather patterns and pest infestations have led to reduced yields. This has inadvertently increased the country’s reliance on imports. But, with the global supply chain issues, how will India balance its domestic production with its import needs?
3. Changing Dietary Preferences: With a growing middle class and increased awareness about health and nutrition, there’s been a surge in the demand for soy-based products. This demand further fuels the need for increased imports. But, is this trend sustainable in the long run, especially given the supply challenges?
The Tradeoffs and Challenges
Balancing Cost with Demand: While the demand for soy-based products rises, the increased costs due to supply chain disruptions present a significant challenge. India must find a way to balance the rising costs with the growing demand. This might involve looking at alternative sources or investing more in domestic production. But, what are the long-term implications of these choices?
Sustainability Concerns: With the increased demand for soybeans, there’s also a growing concern about the environmental impact of soybean farming. Large-scale soybean cultivation can lead to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. Is India ready to address these environmental challenges while meeting its soybean needs?
Navigating International Relations: Trade isn’t just about commodities; it’s also about relationships. India’s choices in sourcing its soybeans can have diplomatic implications. How will India navigate its international relations while meeting its soybean needs?
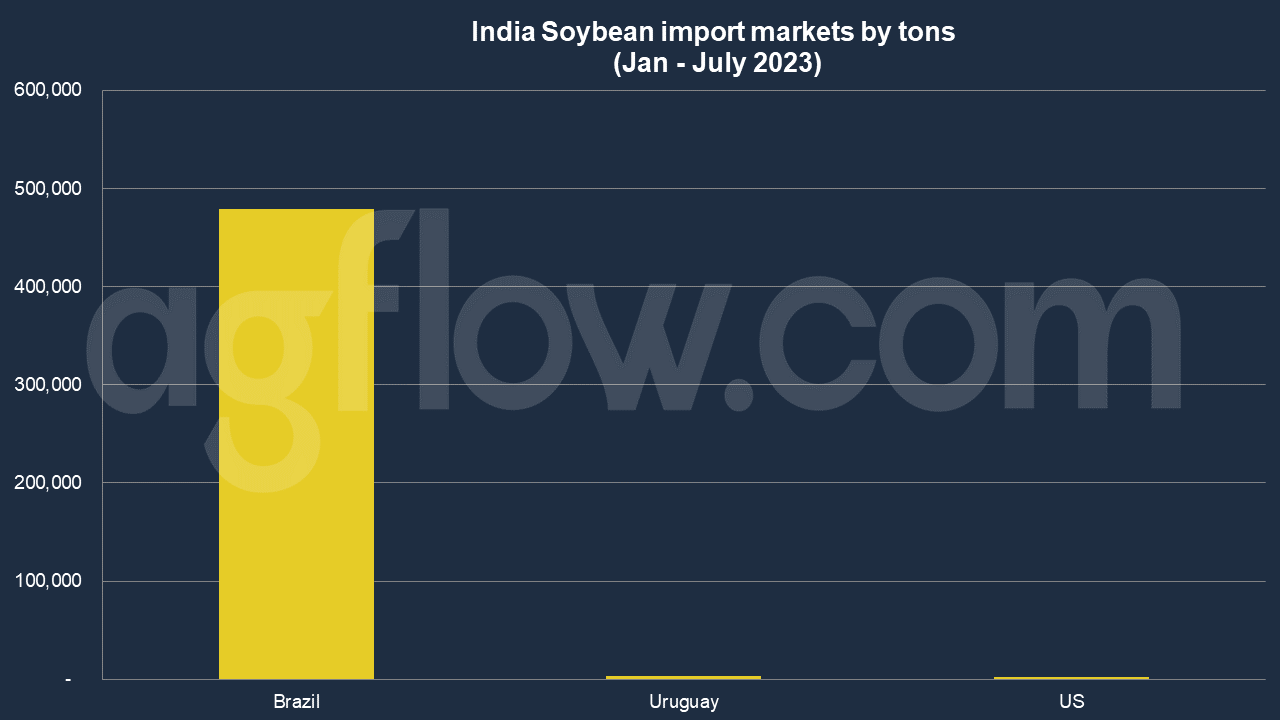
According to AgFlow data, India imported 0.5 milion tons of Soybean from Brazil in Jan – July 2023, followed by Uruguay (3,000 tons) and the United States (1,910 tons). Total imports hit 0.5 million tons in Jan-July 2023. India was purchasing large amounts of Soybean from Brazil, such as 69,000 tons and 66,000 tons, respectively. The US ships small amounts of Soybean to India.
June shipments were the largest in Jan – July of 2023, with 0.13 million tons. The following months were July (0.12 million tons), Apr (0.11 million tons), May (0.1 million tons), and Feb (3,465 tons).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dynamics of India’s soybean imports in 2023 are influenced by a myriad of factors, from global supply chain disruptions to changing dietary preferences. The challenges are manifold, and the solutions are not straightforward. As India continues to navigate this complex landscape, it will be crucial for both the general public and professionals in the agricultural commodity industry to stay informed, adaptive, and forward-thinking.
Try AgFlow Free
Access Free On Updates for Corn, Wheat, Soybean,
Barley, and Sunflower Oil.
No Credit Card Required & Unlimited Access In Time

